Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

उत्तर
Mass of each block is 1 kg, \[\sin \theta_1 = \frac{4}{5}\]
\[\sin \theta_2 = \frac{3}{5}\]
The free-body diagrams for both the boxes are shown below: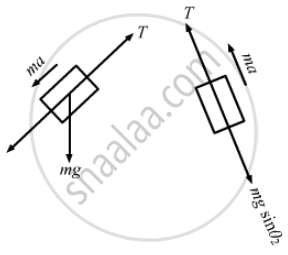
mgsinθ1 − T = ma ...(i)
T − mgsinθ2 = ma ...(ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii),we get:
mg(sinθ1 − sinθ2) = 2ma
⇒ 2a = g (sinθ1 − sinθ2)
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{g}{5} \times \frac{1}{2}\]
\[ = \frac{g}{10}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
What causes motion in a body?
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
