Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
उत्तर

For m1 to be at rest, a1 = 0.
T − m1g = 0
T = m1g ...(i)
For mass m2,
T/2 − 2g = 2a
T = 4a + 4g ...(ii)
For mass m3,
3g – T/2= 2a
T = 6g − 6a ...(ii)
From equations (ii) and (iii), we get:
3T – 12g = 12g – 2T
T = 24g/5= 4.08g
Putting the value of T in equation (i), we get:
m1 = 4.8kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
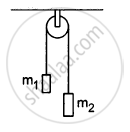
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
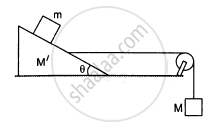
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
