Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
उत्तर
a = 3.26 m/s2, T = 3.9 N
After 2 s, velocity of mass m1,
v = u + at = 0 + 3.26 × 2
= 6.52 m/s upward
At this time, m2 is moving 6.52 m/s downward.
At time 2 s, m2 stops for a moment. But m1 is moving upward with velocity 6.52 m/s. It will continue to move till final velocity (at highest point) becomes zero.
Here, v = 0, u = 6.52 m/s
a = −g = − 9.8 m/s2
v = u + at = 6.52 + (−9.8)t
\[\Rightarrow t = \frac{6 . 52}{9 . 8} \approx \frac{2}{3} \sec\]
After this time, the mass m1 also starts moving downward.
So, the string becomes tight again after \[\frac{2}{3} s\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
The figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. The force acting on the particle is zero in the region
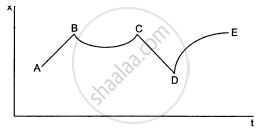
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) CD
(d) DE
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
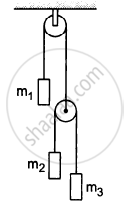
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
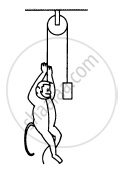
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
The unit of linear momentum is :
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
