Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
उत्तर
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
Tension in the cable = Weight of the elevator
Or, total upward force = total downward force
That is, there's no acceleration or uniform velocity.
So, the elevator is going up/down with uniform speed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
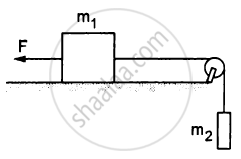
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
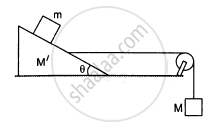
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
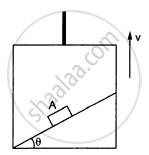
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
