Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
उत्तर
The force of friction acting between my feet and ground is responsible for my deceleration.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
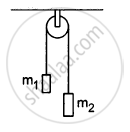
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
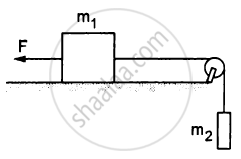
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
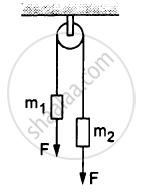
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
How long will it take to fall to the foot of the cliff?
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

