Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If you jump barefoot on a hard surface, your legs are injured. But they are not injured if you jump on a soft surface like sand or pillow. Why?
उत्तर
In both the cases, change in momentum is same but the time interval during which momentum changes to zero is less in the first case. So, by `"F"="dp"/"dt"`, force in the first case will be more. That's why we are injured when we jump barefoot on a hard surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman hits a cricket ball which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because ______.
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of motion.
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
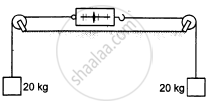
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
The force exerted by the floor of an elevator on the foot of a person is more than the weight of the person if the elevator is
(a) going up and slowing down
(b) going up and speeding up
(c) going down and slowing down
(d) going down and speeding up
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
When a train starts, the head of a standing passenger seems to be pushed backward. Analyse the situation from the ground frame. Does it really go backward? Coming back to the train frame, how do you explain the backward movement of the head on the basis of Newton's laws?
Derive the relation between newton and dyne.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
Name the different kinds of inertia an object can possess. Give an example of each.
Define one Newton.
Classify the types of force based on their application.
Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
