Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
विकल्प
F1 must be equal to F2.
F1 may be equal to F2.
F1 must be unequal to F2
उत्तर
F1 may be equal to F2.
Any force applied in the direction opposite the motion of the particle decelerates it to rest.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
State Newton’s first law of motion. Give two examples to illustrate Newton’s first law of motion.
Define one newton force.
Name the law involved in the following situation :
if there were no friction and no air resistance, then a moving bicycle would go on moving for ever.
The acceleration of a particle is zero, as measured from an inertial frame of reference. Can we conclude that no force acts on the particle?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
If you jump barefoot on a hard surface, your legs are injured. But they are not injured if you jump on a soft surface like sand or pillow. Why?
State Newton's first law of motion.
Give qualitative definition of force on the basic of Newton's first law of motion.
Explain the following :
After alighting from a moving bus , one has to run for some distance in the direction of bus in order to avoid falling .
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
Give one example each of inertia of rest and inertia of motion.
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of a body |
| Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| Law of conservation of linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
A car of mass m starts from rest and acquires a velocity along east `v = vhati (v > 0)` in two seconds. Assuming the car moves with uniform acceleration, the force exerted on the car is ______.
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

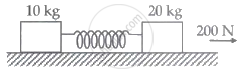
The masses of 10 kg and 20 kg, respectively, are connected by massless spring as shown in the figure. A force of 200 N acts on the 20 kg mass. At the instant shown, the 10 kg mass has acceleration of 12 m/s2. What is the acceleration of 20 kg mass?
(g = 10 m/s2)
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
