Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Newton’s first law of motion. Give two examples to illustrate Newton’s first law of motion.
उत्तर
According to Newton’s first law of motion:
A body at rest will remain at rest and a body in motion will continue in motion in a straight line with a constant velocity, unless it is compelled by an external force to change its state of rest or of uniform motion.
Examples:
(a) A book lying on a table cannot change its state of rest unless an external force is applied on the book.
(b) A car set free on a sloppy road will continue to be in motion unless an external force applied by hands or brakes to bring the car to rest.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it. But Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it. How do you explain the bicycle case ?
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
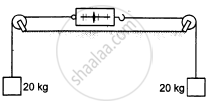
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
A reference frame attached to the earth
(a) is an inertial frame by definition
(b) cannot be an inertial frame because the earth is revolving around the sun
(c) is an inertial frame because Newton's laws are applicable in this frame
(d) cannot be an inertial frame because the earth is rotating about its axis.
A particle is observed from two frames S1 and S2. Frame S2 moves with respect to S1with an acceleration a. Let F1 and F2 be the pseudo forces on the particle when seen from S1 and S2, respectively. Which of the following is not possible?
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of rest
When a bus suddenly takes a tum, the passengers are thrown outwards because of
A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB (Figure). Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually, harder and harder in the downward directon so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
