Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
पर्याय
F1 must be equal to F2.
F1 may be equal to F2.
F1 must be unequal to F2
उत्तर
F1 may be equal to F2.
Any force applied in the direction opposite the motion of the particle decelerates it to rest.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of 36 km/h sees a child standing in the middle of the road and brings his vehicle to rest in 4.0 s just in time to save the child. What is the average retarding force on the vehicle? The mass of the three-wheeler is 400 kg and the mass of the driver is 65 kg.
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
Find the acceleration produced by a force of 5 N acting on a mass of 10 kg.
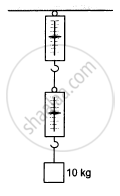
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle's motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
Define one Newton.
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Name the scientist who first stated the law of inertia.
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
Newton's first law of motion describes ______.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

