Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
पर्याय
The two bodies will reach the same height.
A will go higher than B.
B will go higher than A.
Any of the above three may happen depending on the speed with which the objects are thrown.
उत्तर
A will go higher than B.
Let the air exert a constant resistance force = F (in downward direction).
Acceleration of particle A in downward direction due to air resistance, aA = F/mA.
Acceleration of particle B in downward direction due to air resistance, aB = F/mB.
mA > mB
aA < aB
\[S = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2\]
\[So, H_A = ut - \frac{1}{2}( a_A + g) t^2\]
\[H_B = ut - \frac{1}{2}( a_B + g) t^2\]
\[H_A > H_B\]
Therefore, A will go higher than B.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
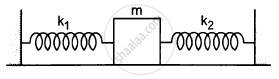
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
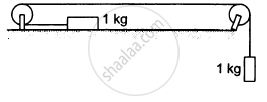
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
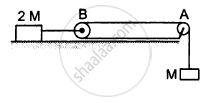
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless.
- Find the acceleration of the mass M.
- Find the tension in the string.
- Calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
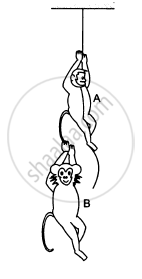
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
