Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
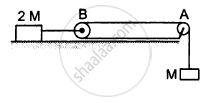
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless.
- Find the acceleration of the mass M.
- Find the tension in the string.
- Calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
उत्तर
Let the acceleration of mass M be a.
So, the acceleration of mass 2M will be \[\frac{a}{2}\]
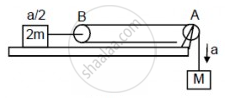
(a)
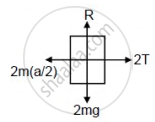
2M(a/2) − 2T = 0
⇒ Ma = 2T
T + Ma − Mg = 0
\[\Rightarrow \frac{Ma}{2} + Ma = Mg \]
\[ \Rightarrow 3Ma = 2Mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{2g}{3}\]
(b) Tension,
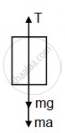
\[T = \frac{Ma}{2} = \frac{M}{2} \times \frac{2g}{3} = \frac{Mg}{3}\]
(c)
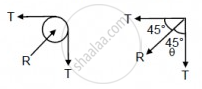
Let T' = resultant of tensions
\[\therefore T' = \sqrt{T^2 + T^2} = \sqrt{2}T\]
\[ \therefore T' = \sqrt{2}T = \frac{\sqrt{2}Mg}{3}\]
\[\text{Again, }\tan\theta = \frac{T}{T} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 45^\circ\]
So, it is `(sqrt2"Mg")/3` at an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
That is the force exerted by the clamp.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
Prove mathematically F = ma
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

