Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
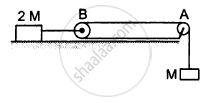
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless.
- Find the acceleration of the mass M.
- Find the tension in the string.
- Calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
Solution
Let the acceleration of mass M be a.
So, the acceleration of mass 2M will be \[\frac{a}{2}\]
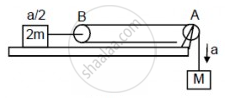
(a)
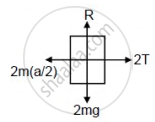
2M(a/2) − 2T = 0
⇒ Ma = 2T
T + Ma − Mg = 0
\[\Rightarrow \frac{Ma}{2} + Ma = Mg \]
\[ \Rightarrow 3Ma = 2Mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{2g}{3}\]
(b) Tension,
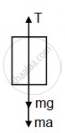
\[T = \frac{Ma}{2} = \frac{M}{2} \times \frac{2g}{3} = \frac{Mg}{3}\]
(c)
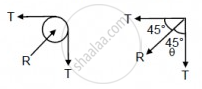
Let T' = resultant of tensions
\[\therefore T' = \sqrt{T^2 + T^2} = \sqrt{2}T\]
\[ \therefore T' = \sqrt{2}T = \frac{\sqrt{2}Mg}{3}\]
\[\text{Again, }\tan\theta = \frac{T}{T} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 45^\circ\]
So, it is `(sqrt2"Mg")/3` at an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
That is the force exerted by the clamp.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
State two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
