Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If you jump barefoot on a hard surface, your legs are injured. But they are not injured if you jump on a soft surface like sand or pillow. Why?
Solution
In both the cases, change in momentum is same but the time interval during which momentum changes to zero is less in the first case. So, by `"F"="dp"/"dt"`, force in the first case will be more. That's why we are injured when we jump barefoot on a hard surface.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of motion.
State Newton’s first law of motion. Give two examples to illustrate Newton’s first law of motion.
Name the physical quantity whose unit is ‘newton’.
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
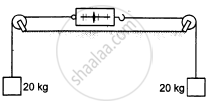
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle's motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
A particle is found to be at rest when seen from a frame S1 and moving with constant velocity when seen from another frame S2. Mark out the possible options.
(a) Both the frames are inertial.
(b) Both the frames are non-inertial.
(c) S1 is inertial and S2 is non-inertial.
(d) S1 is non-inertial and S2 is inertial
Give qualitative definition of force on the basic of Newton's first law of motion.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of rest
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of a body |
| Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| Law of conservation of linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
Classify the types of force based on their application.
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

