Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Classify the types of force based on their application.
Solution
- Like parallel forces
- Unlike parallel forces
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
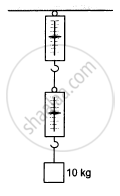
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
If you jump barefoot on a hard surface, your legs are injured. But they are not injured if you jump on a soft surface like sand or pillow. Why?
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
Name the scientist who first stated the law of inertia.
When a bus suddenly takes a tum, the passengers are thrown outwards because of
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
