Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
Solution
a = 3.26 m/s2, T = 3.9 N
After 2 s, velocity of mass m1,
v = u + at = 0 + 3.26 × 2
= 6.52 m/s upward
At this time, m2 is moving 6.52 m/s downward.
At time 2 s, m2 stops for a moment. But m1 is moving upward with velocity 6.52 m/s. It will continue to move till final velocity (at highest point) becomes zero.
Here, v = 0, u = 6.52 m/s
a = −g = − 9.8 m/s2
v = u + at = 6.52 + (−9.8)t
\[\Rightarrow t = \frac{6 . 52}{9 . 8} \approx \frac{2}{3} \sec\]
After this time, the mass m1 also starts moving downward.
So, the string becomes tight again after \[\frac{2}{3} s\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
The figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. The force acting on the particle is zero in the region
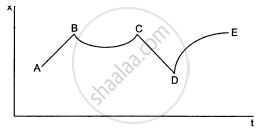
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) CD
(d) DE
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

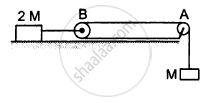
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
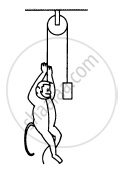
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A body of mass 200 g is moving with a velocity of 5 ms−1. If the velocity of the body changes to 17 ms−1, calculate the change in linear momentum of the body.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

