Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

Solution
Mass per unit length \[= \frac{3}{30} kg/cm\] = 0.10 kg/cm
Mass of the 10 cm part, m1 = 1 kg
Mass of the 20 cm part, m2 = 2 kg
Let F = contact force between them.
From the free-body diagram,
\[m_1 a = F - 20 . . . \left( i \right)\]
\[ m_2 a = 32 - F . . . \left( ii \right) \]
\[\text{ Adding both the equations, we get: }\]
\[a = \frac{12}{m_1 + m_2} = \frac{12}{3} = 4 m/ s^2\]
So, contact force,
F = 20 + 1a
F = 20 + 4 = 24 N
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
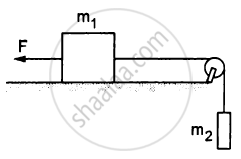
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
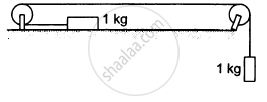
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
State two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

