Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body of mass 200 g is moving with a velocity of 5 ms−1. If the velocity of the body changes to 17 ms−1, calculate the change in linear momentum of the body.
Solution
Mass of body = m = 200 g = 0.2 kg
Velocity = v1 = 5 ms−1; Velocity = v2 = 17 ms−1
Change in linear momentum of body
= mv2 – mv1= m (v2 – v1)
= 0.2(17-5)
= 2.4 Ns or kg ms−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
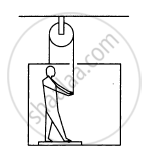
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
