Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
उत्तर
Here, m = 70 kg, g = 10 m/s2
In each instance, the weighing machine measures the reaction R, which represents the apparent weight.
(a) When the lift moves upwards with a uniform speed, acceleration a = 0.
R = mg = 70 x 10 = 700 N
(b) When the lift moves downward with a = 5 ms-2
R = m (g - a) = 70 (10 - 5) = 350 N
(c) When the lift moves upwards with a = 5 ms-2
R = m (g + a) = 70 (10 + 5) = 1050 N
(d) If the lift were to come down freely under gravity, downward acceleration. a = g
∴ R = m (g - a) = m (g - g) = zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
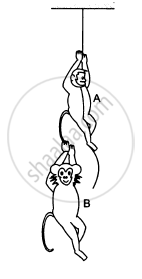
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
