Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
विकल्प
mg
mg/cosθ
mg cosθ
mg tanθ
उत्तर
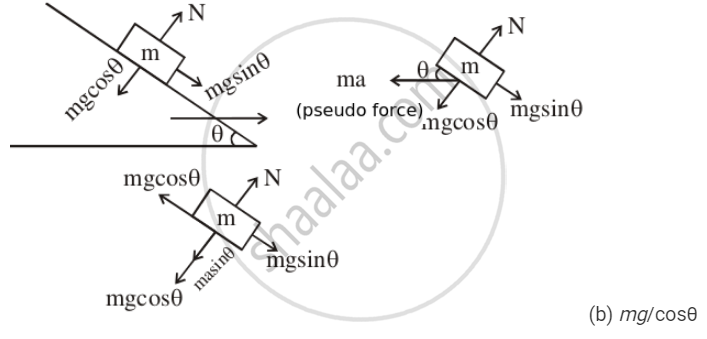
Free-body Diagram of the Small Block of Mass 'm'
The block is at equilibrium w.r.t. to wedge. Therefore,
mg sinθ = ma cosθ
⇒ a = gtanθ
Normal reaction on the block is
N = mg cosθ + ma sinθ
Putting the value of a, we get:
N = mg cosθ + mg tanθsinθ
\[N = mg\cos\theta + mg\frac{\sin\theta}{\cos\theta}\sin\ \theta N=\frac{mg}{\cos\theta}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
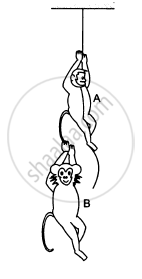
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
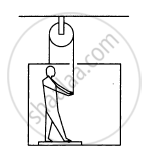
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
What causes motion in a body?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
