Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

उत्तर १
Case (a)
Mass of the monkey, m = 40 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s
Maximum tension that the rope can bear, Tmax = 600 N
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 6 m/s2 upward
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T – mg = ma
∴T = m(g + a)
= 40 (10 + 6)
= 640 N
Since T > Tmax, the rope will break in this case.
Case (b)
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 4 m/s2 downward
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
mg – T = ma
∴T = m (g – a)
= 40(10 – 4)
= 240 N
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
Case (c)
The monkey is climbing with a uniform speed of 5 m/s. Therefore, its acceleration is zero, i.e., a = 0.
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T – mg = ma
T – mg = 0
∴T = mg
= 40 × 10
= 400 N
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
Case (d)
When the monkey falls freely under gravity, its will acceleration become equal to the acceleration due to gravity, i.e., a = g
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
mg – T = mg
∴T = m(g – g) = 0
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
उत्तर २
(a) When the monkey climbs up with an acceleration a, then T – mg = ma where T represents the tension in figure.
:. T = mg + ma = m (g +a)
or T = 40 kg(10 + 6) ms^(-2) = 640 N
But the rope can withstand a maximum tension of 600 N. So the rope will break
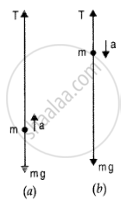
b) When the monkey is climbing down with an acceleration, then
mg - T =ma (Figure b)
=> T = mg - ma = m(g -a)
or T = 40 kg x (10 - 4) `ms^2` = 240 N
(c) When the monkey climbs up with uniform speed, then T mg = 40 kg x 10 ms-2 = 400 N The rope will hot break.
(d) When the monkey is falling freely, it would be a state of weightlessness. So, tension will be zero and the rope will not break.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Prove mathematically F = ma
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

