Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

Solution 1
Case (a)
Mass of the monkey, m = 40 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s
Maximum tension that the rope can bear, Tmax = 600 N
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 6 m/s2 upward
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T – mg = ma
∴T = m(g + a)
= 40 (10 + 6)
= 640 N
Since T > Tmax, the rope will break in this case.
Case (b)
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 4 m/s2 downward
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
mg – T = ma
∴T = m (g – a)
= 40(10 – 4)
= 240 N
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
Case (c)
The monkey is climbing with a uniform speed of 5 m/s. Therefore, its acceleration is zero, i.e., a = 0.
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T – mg = ma
T – mg = 0
∴T = mg
= 40 × 10
= 400 N
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
Case (d)
When the monkey falls freely under gravity, its will acceleration become equal to the acceleration due to gravity, i.e., a = g
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
mg – T = mg
∴T = m(g – g) = 0
Since T < Tmax, the rope will not break in this case.
Solution 2
(a) When the monkey climbs up with an acceleration a, then T – mg = ma where T represents the tension in figure.
:. T = mg + ma = m (g +a)
or T = 40 kg(10 + 6) ms^(-2) = 640 N
But the rope can withstand a maximum tension of 600 N. So the rope will break
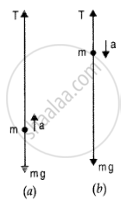
b) When the monkey is climbing down with an acceleration, then
mg - T =ma (Figure b)
=> T = mg - ma = m(g -a)
or T = 40 kg x (10 - 4) `ms^2` = 240 N
(c) When the monkey climbs up with uniform speed, then T mg = 40 kg x 10 ms-2 = 400 N The rope will hot break.
(d) When the monkey is falling freely, it would be a state of weightlessness. So, tension will be zero and the rope will not break.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.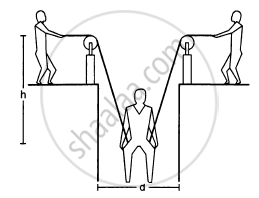
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
