Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
उत्तर
Initial velocity, u = 30 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0
Time, t = 2s
Force, F = 1500 N
Here, a = (v - u)/t = (0 - 30)/ 2 = - 15 ms-2. Here, negative sign indicates retardation.
Now, F = ma.
Or, m = F/a = (1500/ 15) = 100 kg.
Change in momentum = Final momentum - Initial momentum
Or, Δp = m (v - u)
Or, Δp = 100 (0 - 30)
Or, Δp = 3000 kg m/s-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
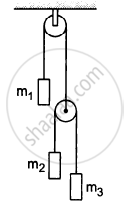
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Prove mathematically F = ma
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
