Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
Options
the force acting on the scale is zero, but a torque about the centre of mass can act on the scale.
the force acting on the scale is zero and the torque acting about centre of mass of the scale is also zero.
the total force acting on it need not be zero but the torque on it is zero.
neither the force nor the torque need to be zero.
Solution
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies the force acting on the scale is zero and the torque acting about centre of mass of the scale is also zero.
Explanation:
Since the body is moving with a uniform velocity, hence its acceleration is zero. This implies that the net force acting on it must be zero, which further makes the torque acting about the centre of mass of the scale also zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m away from the open end as shown in Figure. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface below it is 0.15. On a straight road, the truck starts from rest and accelerates with 2 m s–2. At what distance from the starting point does the box fall off the truck? (Ignore the size of the box).

A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
The figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. The force acting on the particle is zero in the region
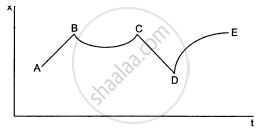
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) CD
(d) DE
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
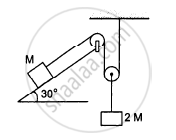
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
