Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
Options
zero
`-(0.45 hati + 0.6 hatj)`
`-(0.9 hati + 1.2 hatj)`
`-5 (hati + hatj)`
Solution
`-(0.9 hati + 1.2 hatj)`
Explanation:
Given, `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m/s
And `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m/s
Mass of the ball = 150 g = 0.15 kg
Δp = Change in momentum
= Final momentum – Initial momentum
= `mv - mu`
= `m(v - u) = (0.15) [- (3hati + 4hatj) - (3hati + 4hatj)]`
= `(0.15) xx [ - 6hati - 8hatj]`
= `- [0.15 xx 6hati + 0.15 xx 8hatj]`
= `- [0.9 hati + 1.20 hatj]`
Hence, Δp = `-[0.9 hati + 1.2 hatj]`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
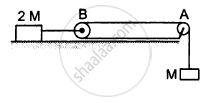
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
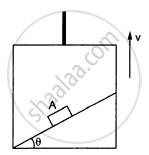
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
