Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
Solution
Initial velocity of the electrons is negligible, i.e. u = 0.
Final velocity of the electrons, v = 5 × 106 m/s
Distance travelled by the electrons,
s = 1 cm = 1 × 10−2 m
∴ Acceleration, \[a = \frac{v^2 - u^2}{2 S}\]
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{\left( 5 \times {10}^5 \right)^2 - 0}{2 \times 1 \times {10}^{- 3}} = \frac{25 \times {10}^{12}}{2 \times {10}^{- 2}}\]
So, force on the electrons, F = ma
⇒ F = 9.1 × 10−31 × 12.5 × 10−14
= 1.1 × 10−15 N
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
The figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. The force acting on the particle is zero in the region
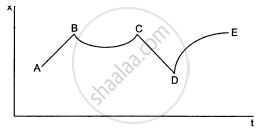
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) CD
(d) DE
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
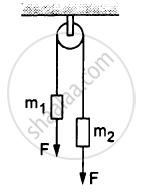
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
What causes motion in a body?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
