Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
उत्तर
The given situation can be represented as shown in the following figure.
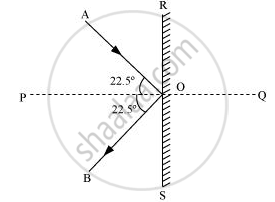
Where,
AO = Incident path of the ball
OB = Path followed by the ball after deflection
∠AOB = Angle between the incident and deflected paths of the ball = 45°
∠AOP = ∠BOP = 22.5° = θ
Initial and final velocities of the ball = v
Initial velocity's horizontal component = vcos θ along RO
Initial velocity's vertical component = vsin θ along PO
Final velocity's horizontal component = vcos θ along OS
Final velocity's vertical component = vsin θ along OP
The horizontal velocity components remain unchanged. The vertical velocity components are directed oppositely.
∴Impulse imparted to the ball = Change in the linear momentum of the ball
`= mvcostheta - (- mvcos theta)`
`= 2mvcos theta`
Mass of the ball, m = 0.15 kg
Velocity of the ball, v = 54 km/h = 15 m/s
∴ Impulse = 2 × 0.15 × 15 cos 22.5° = 4.16 kg m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.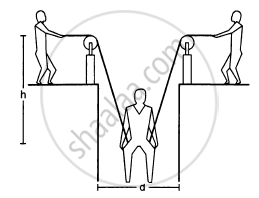
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

The force of buoyancy exerted by the atmosphere on a balloon is B in the upward direction and remains constant. The force of air resistance on the balloon acts opposite the direction of velocity and is proportional to it. The balloon carries a mass M and is found to fall to the earth's surface with a constant velocity v. How much mass should be removed from the balloon so that it may rise with a constant velocity v?
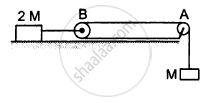
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
Prove mathematically F = ma
