Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
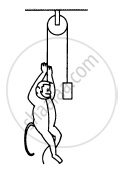
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
उत्तर
Suppose the monkey accelerates upward with acceleration a and the block accelerates downward with acceleration a1.
Let force exerted by the monkey be F.
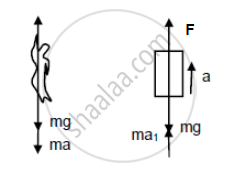
From the free-body diagram of the monkey, we get:
F− mg − ma = 0 ...(i)
⇒ F = mg + ma
Again, from the free-body diagram of the block,
F + ma1 − mg = 0
mg + ma + ma1 − mg = 0 [From (i)]
⇒ ma = −ma1
⇒ a = −a1
If acceleration −a1 is in downward direction then the acceleration a1 will be in upward direction.
This implies that the block and the monkey move in the same direction with equal acceleration.
If initially they were at rest (no force is exerted by the monkey), then their separation will not change as time passes because both are moving same direction with equal acceleration.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
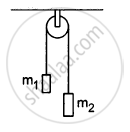
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
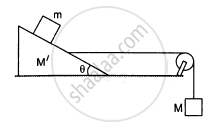
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
How long will it take to fall to the foot of the cliff?
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

