Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
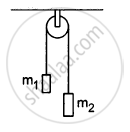
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
उत्तर
The masses of the blocks are m1 = 0.3 kg and m2 = 0.6 kg
The free-body diagrams of both the masses are shown below: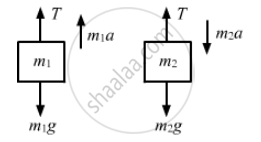
For mass m1,
T − m1g = m1a ...(i)
For mass m2,
m2g − T= m2a ...(ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we get:
g(m2 − m1) = a(m1 + m2)
\[\Rightarrow a = g{\left( \frac{m_2 - m_1}{m_1 + m_2} \right)}$\]
\[ = 9 . 8 \times \frac{0 . 6 - 0 . 3}{0 . 6 + 0 . 3}\]
\[ = 3 . 266 m/ s^2\]
(a) t = 2 s, a = 3.266 ms−2, u = 0
So, the distance travelled by the body,
\[S = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2 \]
\[ = 0 + \frac{1}{2}\left( 3 . 266 \right) 2^2 = 6 . 5 m\]
(b) From equation (i),
T = m1 (g + a)
= 0.3 (9.8 + 3.26) = 3.9 N
(c)The force exerted by the clamp on the pulley,
F = 2T = 2 × 3.9 = 7.8 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. The force acting on the particle is zero in the region
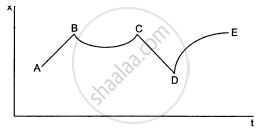
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) CD
(d) DE
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

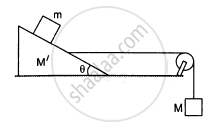
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

