Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
उत्तर १
(a) Mass of the helicopter, mh = 1000 kg
Mass of the crew and passengers, mp = 300 kg
Total mass of the system, m = 1300 kg
Acceleration of the helicopter, a = 15 m/s2
Using Newton’s second law of motion, the reaction force R, on the system by the floor can be calculated as:
R – mpg = ma
= mp(g + a)
= 300 (10 + 15) = 300 × 25
= 7500 N
Since the helicopter is accelerating vertically upward, the reaction force will also be directed upward. Therefore, as per Newton’s third law of motion, the force on the floor by the crew and passengers is 7500 N, directed downward.
(b) Using Newton’s second law of motion, the reaction force R’, experienced by the helicopter can be calculated as:
R' - mg = ma
=m(g+a)
=1300(10+15) = 1300 xx 25
= 32500 N
The reaction force experienced by the helicopter from the surrounding air is acting upward. Hence, as per Newton’s third law of motion, the action of the rotor on the surrounding air will be 32500 N, directed downward.
(c) The force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air is 32500 N, directed upward.
उत्तर २
Here, mass of helicopter, m1= 1000 kg
Mass of the crew and passengers, m2 = 300 kg upward acceleration, a = 15 ms-2and g = 10 ms-2
(a)Force on the floor of helicopter by the crew and passengers = apparent weight of crew and passengers
= m2 (g + a) = 300 (10 + 15) N = 7500 N
(b)Action of rotor of helicopter on surrounding air is obviously vertically downwards, because helicopter rises on account of reaction to this force. Thus, force of action
F = (m1+ m2) (g + a) = (1000 + 300) (10 + 15) = 1300 x 25 = 32500 N
(c)Force on the helicopter due to surrounding air is the reaction. As action and reaction are equal and opposite, therefore, force of reaction, F = 32500 N, vertically upwards.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
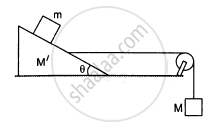
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
