Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
उत्तर
Mass of body = m = 0.5 kg
Linear momentum = P = 5 Ns
Velocity of body = v = ?
We know P = mv
v = `"P"/"m"=5/0.5`
v = 10 ms−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
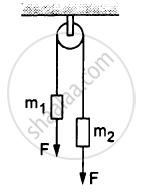
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
