Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
उत्तर १
(a) Mass of the block, m = 15 kg
Coefficient of static friction, μ = 0.18
Acceleration of the trolley, a = 0.5 m/s2
As per Newton’s second law of motion, the force (F) on the block caused by the motion of the trolley is given by the relation:
F = ma = 15 × 0.5 = 7.5 N
This force is acted in the direction of motion of the trolley.
Force of static friction between the block and the trolley:
f = μmg
= 0.18 × 15 × 10 = 27 N
The force of static friction between the block and the trolley is greater than the applied external force. Hence, for an observer on the ground, the block will appear to be at rest.
When the trolley moves with uniform velocity there will be no applied external force. Only the force of friction will act on the block in this situation.
(b) An observer, moving with the trolley, has some acceleration. This is the case of non-inertial frame of reference. The frictional force, acting on the trolley backward, is opposed by a pseudo force of the same magnitude. However, this force acts in the opposite direction. Thus, the trolley will appear to be at rest for the observer moving with the trolley.
उत्तर २
(a) Force experienced by block, F = ma = 15 x 0.5 = 7.5 N Force of friction,Ff= p mg = 0.18 x 15 x 10 = 27 N. i.e., force experienced by block will be less than the friction.So the block will not move. It will remain stationary w.r.t. trolley for a stationary observer on ground.
(b) The observer moving with trolley has an accelerated motion i.e., he forms non-inertial frame in which Newton’s laws of motion are not applicable. The box will be at rest relative to the observer.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
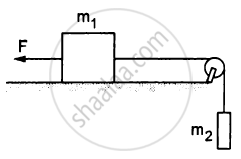
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
