Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
उत्तर
Initial velocity, u = 20 m/s
Time, t = 2s
g = 10 m/s2
Maximum height reached in 2s, H = (1/2) gt2
Or, H = (1/2) (10) (2) 2
Or, H = 20 m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

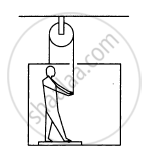
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

