Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
विकल्प
x + v t
x − v t
x
depends on the direction of the train
उत्तर
x
The moving train does not put any extra force on the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus. So, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, will be same as before, i.e. x.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
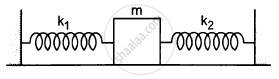
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.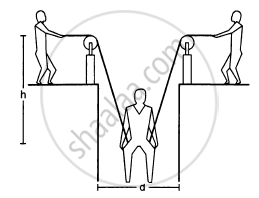
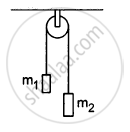
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
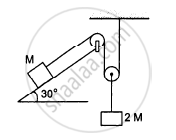
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
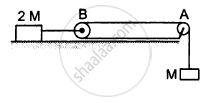
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
The unit of linear momentum is :
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
A body of mass 200 g is moving with a velocity of 5 ms−1. If the velocity of the body changes to 17 ms−1, calculate the change in linear momentum of the body.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
