Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
उत्तर
Force, F = 10 N
Mass, m = 2 kg
Time, t = 3 s
Initial velocity, u = 0 m/s.
Change in momentum = Final momentum - initial momentum
Δp = mv - mu.
Or, Δp = m (v - u).
Or, Δp = 2 (15 - 0) = 30 kg m/s-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
Consider the Atwood machine of the previous problem. The larger mass is stopped for a moment, 2.0 s after the system is set into motion. Find the time that elapses before the string is tight again.
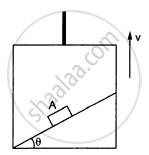
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
