Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB (Figure). Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually, harder and harder in the downward directon so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?

Solution
The thread AB will break earlier than the thread CD. This is because forces acting on thread CD = applied force and force acting on thread AB = (applied force + weight of 2 kg mass). Hence, the force acting on thread AB is larger than the force acting on thread CD.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of 36 km/h sees a child standing in the middle of the road and brings his vehicle to rest in 4.0 s just in time to save the child. What is the average retarding force on the vehicle? The mass of the three-wheeler is 400 kg and the mass of the driver is 65 kg.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
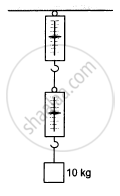
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
Explain the following :
After alighting from a moving bus , one has to run for some distance in the direction of bus in order to avoid falling .
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of motion
Classify the types of force based on their application.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

