Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A burner raises the temperature of 360 g of water from 40°C to 100°C in 5 minutes. Calculate the rate of heat supplied by the burner.
उत्तर
m = 360 g = O .36 kg
Change in temperature, ΔT = (100 - 40)°C = 60°C = 60 K
Amount of heat required, Q = m x C x ΔT
= 0.36 x 4200 x 60 = 90720 J
Time taken = 5 min = 300 sec
Rate of heat supplied = `"Q"/"t" = 90720/300` = 302.4 J/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Heat supplied to a solid change it into liquid. What is this change in the phase called?
Why do the farmers fill their fields with water on a cold winter night?
(i) State whether the specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same when its state changes from solid to liquid.
(ii) Give one example to support your answer.
Explain, why temperature in hot summer, falls sharply after a sharp shower?
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1. Which of the two is a good conductor of heat? How is one led to this conclusion?
Why are athletes advised to put on extra clothes after competing on event?
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
Numerical Problem.
How much heat energy is required to change 2 kg of ice at 0°C into water at 20°C? (Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 3,34,000 J/kg, Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 JKg–1K–1).
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
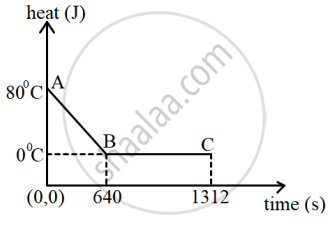
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Match the columns:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| The SI unit of specific heat capacity | (a) Jkg−1°C−1 |
| (b) kg/m3 | |
| (c) calorie |
