Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a battery of V volts. The charge stored in it is 300 μC. When potential across the capacitor is reduced by 100 V, the charge stored in it becomes 100 μC. Calculate The potential V and the unknown capacitance. What will be the charge stored in the capacitor if the voltage applied had increased by 100 V?
उत्तर
(i) Initial voltage, V1 = V volts, Charge stored,Q1 = 300 µC
Q1 = CV1 ..(1)
Changed potential, V2 = V-100 V
Q2 = 100 µC
Q2 = CV2 ..(2)
By dividing (2) from (1), we get `(Q_1)/(Q_2) = (CV_1)/(CV_2) => Q_1/Q_2 = V_1 /V_2`
`=> 300/100 = V/(V- 100) => V = 150 \text { volts }`
`∴ C = Q_1/V_1 = (300 xx 10^-6)/150 = 2 xx 10^-6 F = 2 μ F`
(ii) If the voltage applied had increased by 120 V, then V3 = 150+100 = 250 V
Hence, charge stored in the capacitor, Q3 = CV3 = 2×10-6×250 = 500 µC
(ii) If the voltage applied had increased by 120 V, then V3 = 150+100 = 250 V
Hence, charge stored in the capacitor, Q3 = CV3 = 2×10-6×250 = 500 µC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ is being charged by connecting it across a dc source along with an ammeter. Will the ammeter show a momentary deflection during the process of charging? If so, how would you explain this momentary deflection and the resulting continuity of current in the circuit? Write the expression for the current inside the capacitor.
A thin metal plate P is inserted between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance C in such a way that its edges touch the two plates . The capacitance now becomes _________ .
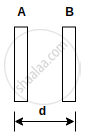
A parallel-plate capacitor has plate area 25⋅0 cm2 and a separation of 2⋅00 mm between the plates. The capacitor is connected to a battery of 12⋅0 V. (a) Find the charge on the capacitor. (b) The plate separation is decreased to 1⋅00 mm. Find the extra charge given by the battery to the positive plate.
Take `C_1 = 4.0 "uF" and C_2 = 6.0 "uF"` in figure . Calculate the equivalent capacitance of the combination between the points indicated.

Each of the plates shown in figure has surface area `(96/∈_0) xx 10^-12` Fm on one side and the separation between the consecutive plates is 4⋅0 mm. The emf of the battery connected is 10 volts. Find the magnitude of the charge supplied by the battery to each of the plates connected to it.
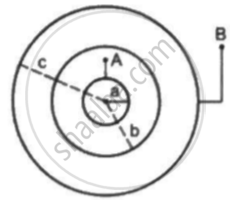
Suppose the space between the two inner shells is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant K. Find the capacitance of the system between A and B.
A parallel-plate capacitor with the plate area 100 cm2 and the separation between the plates 1⋅0 cm is connected across a battery of emf 24 volts. Find the force of attraction between the plates.
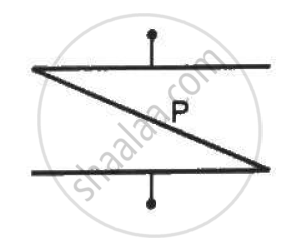
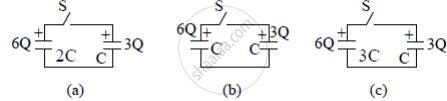
Three circuits, each consisting of a switch 'S' and two capacitors, are initially charged, as shown in the figure. After the switch has been closed, in which circuit will the charge on the left-hand capacitor
(i) increase,
(ii) decrease, and
(iii) remains the same? Give reasons.
During a thunder storm, the movement of water molecules within the clouds creates friction, partially causing the bottom part of the clouds to become negatively charged. This implies that the bottom of the cloud and the ground act as a parallel plate capacitor. If the electric field between the cloud and ground exceeds the dielectric breakdown of the air (3 × 106 Vm–1), lightning will occur.

- If the bottom part of the cloud is 1000 m above the ground, determine the electric potential difference that exists between the cloud and ground.
- In a typical lightning phenomenon, around 25 C of electrons are transferred from cloud to ground. How much electrostatic potential energy is transferred to the ground?
Two plates A and B of a parallel plate capacitor are arranged in such a way, that the area of each plate is S = 5 × 10-3 m 2 and distance between them is d = 8.85 mm. Plate A has a positive charge q1 = 10-10 C and Plate B has charge q2 = + 2 × 10-10 C. Then the charge induced on the plate B due to the plate A be - (....... × 10-11 )C