Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A hollow cylindrical box of length 0.5 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 20 xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
उत्तर
(i) Given,
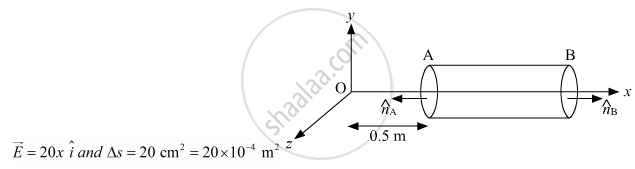
As the electric field is only along the x-axis, so, flux will pass only through the cross-section of cylinder.
Magnitude of electric field at A,
`E_A = 20 xx 0.5 = 10 N C^-1`
Magnitude of lelectic field at cross - section B
EB = 20 × 1= 20 NC-1
The corresponding eletric fluxes are
`phi_A = vecE.Δvecs = 10 xx 20 xx 10^-4 xx cos 180° = - 0.02 N m^2 C^-1`
`phi_B = vecE.Δvecs = 20 xx 20 xx 10^-4 xx cos0° = 0.04 N m^2 C^-1`
So, the net flux through the cylinder,
`phi = phi _A + phi_B = - 0.02 + 0.04 = 0.02 N m^2 C^-1 xx 10^12C`
(ii) Using Gauss’s law:
`oint vecE. vecds = q/in_0 => 0.02 = q/(8.85 xx 10^-12) => q =8.85 xx 0.02 xx 10^-12 = 0.177 xx 10^12 C`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider a system of n charges q1, q2, ... qn with position vectors `vecr_1,vecr_2,vecr_3,...... vecr_n`relative to some origin 'O'. Deduce the expression for the net electric field`vec E` at a point P with position vector `vecr_p,`due to this system of charges.
The electric field at the origin is along the positive x-axis. A small circle is drawn with the centre at the origin, cutting the axes at points A, B, C and D with coordinates (a, 0), (0, a), (−a, 0), (0, −a), respectively. Out of the points on the periphery of the circle, the potential is minimum at
A point charge q is rotated along a circle in an electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
Electric potential decreases uniformly from 120 V to 80 V, as one moves on the x-axis from x = −1 cm to x = +1 cm. The electric field at the origin
(a) must be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(b) may be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(c) may be greater than 20 Vcm−1
(d) may be less than 20 Vcm−1
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How much is the work done by the electric force on the particle during this period?
12 J of work has to be done against an existing electric field to take a charge of 0.01 C from A to B. How much is the potential difference VB − VA?
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
Two identical blocks are kept on a frictionless horizontal table connected by a spring of stiffness k and of original length l0. A total charge Q is distributed on the block such that maximum elongation of spring at equilibrium is equal to x. Value of Q is ______.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
