Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Electric potential decreases uniformly from 120 V to 80 V, as one moves on the x-axis from x = −1 cm to x = +1 cm. The electric field at the origin
(a) must be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(b) may be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(c) may be greater than 20 Vcm−1
(d) may be less than 20 Vcm−1
उत्तर
(b) may be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(c) may be greater than 20 Vcm−1
Change in the electric potential, dV = 40 V
Change in length, \[∆ r\] = −1−1 = −2 cm
Electric field, \[E = \frac{- dV}{dr}\]
\[\Rightarrow E = - \frac{40 V}{- 2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow E = 20 {Vcm}^{- 1}\]
This is the value of the electric field along the x axis.
Electric field is maximum along the direction in which the potential decreases at the maximum rate. But here, direction in which the potential decreases at the maximum rate may or may not be along the x-axis. From the given information,the direction of maximum decrease in potential cannot be found out accurately. So, E can be greater than 20 V/cm in the direction of maximum decrease in potential.
So, the electric field at the origin may be equal to or greater than 20 Vcm−1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
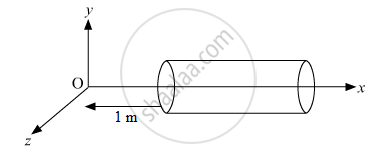
A hollow cylindrical box of length 0.5 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 20 xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
Why does a phonograph record attract dust particles just after it is cleaned?
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
A point charge q is rotated along a circle in an electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
Which of the following quantities does not depend on the choice of zero potential or zero potential energy?
The electric field in a region is directed outward and is proportional to the distance rfrom the origin. Taking the electric potential at the origin to be zero,
Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R. Find the point on the axis where the electric field is maximum.
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. Find the electric force and the force of gravity acting on this particle. Can one of these forces be neglected in comparison with the other for approximate analysis?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
A ball of mass 100 g and with a charge of 4.9 × 10−5 C is released from rest in a region where a horizontal electric field of 2.0 × 104 N C−1 exists. (a) Find the resultant force acting on the ball. (b) What will be the path of the ball? (c) Where will the ball be at the end of 2 s?
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 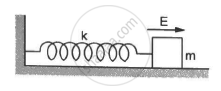
Consider the situation of the previous problem. A charge of −2.0 × 10−4 C is moved from point A to point B. Find the change in electrical potential energy UB − UA for the cases (a), (b) and (c).
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
Two identical blocks are kept on a frictionless horizontal table connected by a spring of stiffness k and of original length l0. A total charge Q is distributed on the block such that maximum elongation of spring at equilibrium is equal to x. Value of Q is ______.
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is ______.
When 1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes ______.
Two similar spheres having +Q and -Q charges are kept at a certain distance. F force acts between the two. If at the middle of two spheres, another similar sphere having +Q charge is kept, then it experiences a force in magnitude and direction as ______.
