Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A cell-free method of amplifying DNA first developed in the mid 1980's revolutionised the field of biotechnology, Name the method and explain the basic steps of the technique involved.
उत्तर
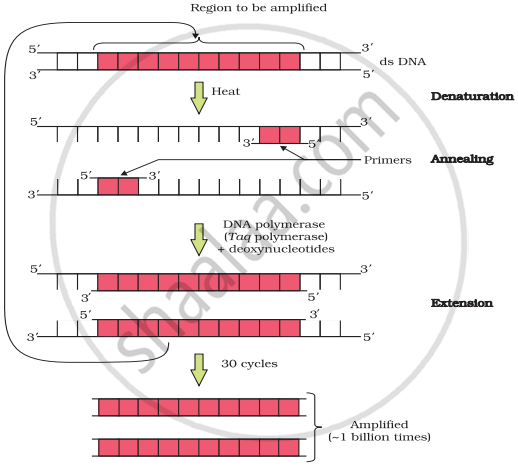
In molecular biology, the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) method is used to multiply a gene or a portion of DNA. It is heavily utilised during the gene-editing process. A primer, a template strand, and a thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus are used in the in-vitro synthesis of sequences. The DNA segment is multiplied by a constant rate of DNA replication to a maximum of 1 billion copies.
- Denaturation: The two strands of the double-stranded DNA molecules are split into a single strand by heating them to a high temperature (94° C). Denaturation is the term for this action. The DNA synthesis process uses each strand as a template.
- Annealing: Since the sequences of the two oligonucleotide primers are complementary to the 3' ends of the template DNA, they anneal (hybridise) to each of the single-stranded DNA templates in this stage. Depending on the length and order of the primers, this step is performed at a lower temperature. The original DNA molecule is duplicated as a result.
- Extension of primers: The primers are extended by DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase) using the nucleotides present in the process. 72°C is the ideal temperature for this polymerization phase. To acquire many copies of the rDNA segment, this procedure is performed several times. The amplified region can be ligated to a vector and used for further cloning. As a result, recombinant DNA is produced (rDNA).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain enzyme – replacement therapy to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency. Mention two disadvantages of this procedure.
How many amino acids are arranged in the two chains of Insulin?
ELISA technique is based on the principles of antigen-antibody interaction. Can this technique be used in the molecular diagnosis of a genetic disorder, such as phenylketonuria?
What are recombinant vaccines? Explain the types.
With regard to insulin choose the correct options.
- C-peptide is not present in mature insulin.
- The insulin produced by rDNA technology has C-peptide.
- The pro-insulin has C-peptide.
- A-peptide and B-peptide of insulin are interconnected by disulphide bridges.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
The Adenosine deaminase deficiency results in ______.
When a foreign DNA is introduced into an organism, how is it maintained in the host and how is it transferred to the progeny of the organism?
How does a gene therapy involving direct modification of the cells, in order to achieve a therapeutic goal is used in the treatment of ADA deficiency? Explain.
The diagram given below represents the schematic structure of proinsulin, which undergoes certain modifications before it becomes a fully functional insulin.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow:
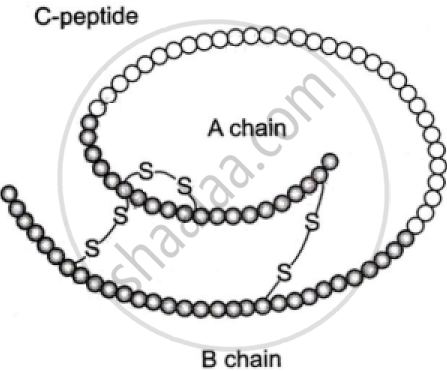
- State the change the proinsulin undergoes to become fully functional.
- Name the modern scientific technique used for the production of human insulin.
- How are the two polypeptide chains of the fully functional insulin held together?
Illustrate using any one example of transgenic bacteria.
