Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A comet orbits the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit. Does the comet have a constant (a) linear speed, (b) angular speed, (c) angular momentum, (d) kinetic energy, (e) potential energy, (f) total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the Sun.
उत्तर १
(a) The linear speed of the comet is variable in accordance with Kepler7s second law. When comet is near the sun, its speed is higher. When the comet is far away from the sun, its speed is very less.
(b) Angular speed also varies slightly.
(c) Comet has constant angular momentum.
(d) Kinetic energy does not remain constant.
(e) Potential energy varies along the path.
(f) Total energy throughout the orbit remains constant.
उत्तर २
(a) No
(b) No
(c) Yes
(d) No
(e) No
(f) Yes
Angular momentum and total energy at all points of the orbit of a comet moving in a highly elliptical orbit around the Sun are constant. Its linear speed, angular speed, kinetic, and potential energy varies from point to point in the orbit.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A Saturn year is 29.5 times the earth year. How far is the Saturn from the sun if the earth is 1.50 ×108 km away from the sun?
Let the period of revolution of a planet at a distance R from a star be T. Prove that if it was at a distance of 2R from the star, its period of revolution will be \[\sqrt{8}\] T.
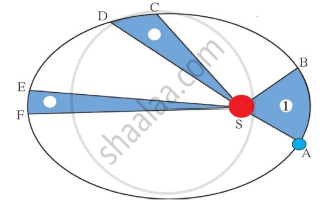
Identify the law shown in the figure and state three respective laws.
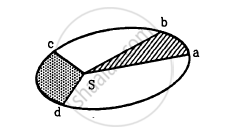
In the Following figure shows the elliptical path of a planet about the sun. The two shaded parts have equal area. If t1 and t2 be the time taken by the planet to go from a to b and from c to d respectively,
Answer the following question.
State Kepler’s law of the period.
The earth moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit as shown in the figure. The ratio, `"OA"/"OB"` = x. The ratio of the speed of the earth at Band at A is ______.

If the sun and the planets carried huge amounts of opposite charges ______.
- all three of Kepler’s laws would still be valid.
- only the third law will be valid.
- the second law will not change.
- the first law will still be valid.
Draw areal velocity versus time graph for mars.
Out of aphelion and perihelion, where is the speed of the earth more and why?
A star like the sun has several bodies moving around it at different distances. Consider that all of them are moving in circular orbits. Let r be the distance of the body from the centre of the star and let its linear velocity be v, angular velocity ω, kinetic energy K, gravitational potential energy U, total energy E and angular momentum l. As the radius r of the orbit increases, determine which of the above quantities increase and which ones decrease.
