Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicularly in a magnetic field. Name the rule which can be used to find the direction of force acting on the conductor.
उत्तर
When a current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field, Fleming's left-hand rule can be used to find the direction of force acting on the conductor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current ______.
State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Describe how you will locate a current-carrying wire concealed in a wall.
List three ways in which the magnetic field strength of a current-carrying solenoid can be increased?
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
For Fleming's left-hand rule, write down the three things that are 90° to each other, and next to each one write down the finger or thumb that represents it.
In the simple electric motor of figure given below, the coil rotates anticlockwise as seen by the eye from the position X when current flows in the coil

Is the current flowing clockwise or anticlockwise around the coil when viewed from above?
The strength of magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor is ____________.
Assertion (A): A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge in the same direction as the direction of the field itself.
Reason (R): The direction of force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
|
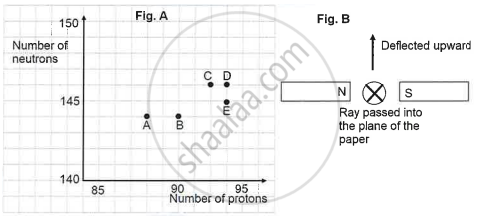
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.