Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) An electron moves along a circle of radius 1 m in a perpendicular magnetic field of strength 0.50 T. What would be its speed? Is it reasonable? (b) If a proton moves along a circle of the same radius in the same magnetic field, what would be its speed?
उत्तर
Given:
(a) Radius of the circle = 1 m
Magnetic field strength = 0.50 T
We know:
`r = (m_ev_e)/(Be)`
`ve = (rBe)/(BE) , "where m_e is mass of the electron of the speed of the electron"`
`= (1 xx0.50xx1.6xx10^-19)/(9.1xx10^10 m/s)`
≈ 8.8 × 1010 m/s
Since, the speed of the electron moving along the circle is greater than the speed of light, it is not reasonable.
(b) For a proton,
`r = (m_pv_p)/(Be)`
`v_p = (rBe)/(m_p)`
where mp is the mass of the proton and vp is its speed.
`r = (1xx0.50xx1.6xx10^-19)/(1.6xx10^-27)`
r = 5 × 107 m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Electrons
(B) Protons
(C) Deuterons
(D) α- particles
Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged particle in a magnetic field and show that it is independent of velocity or energy of the particle.
A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency?
An α-particle and a proton are released from the centre of the cyclotron and made to accelerate.
(i) Can both be accelerated at the same cyclotron frequency?
Give reason to justify your answer.
(ii) When they are accelerated in turn, which of the two will have higher velocity at the exit slit of the does?
Consider a 10-cm long portion of a straight wire carrying a current of 10 A placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T making an angle of 53° with the wire. What magnetic force does the wire experience?
Figure shows a rod PQ of length 20.0 cm and mass 200 g suspended through a fixed point O by two threads of lengths 20.0 cm each. A magnetic field of strength 0.500 T exists in the vicinity of the wire PQ, as shown in the figure. The wires connecting PQ with the battery are loose and exert no force on PQ. (a) Find the tension in the threads when the switch S is open. (b) A current of 2.0 A is established when the switch S is closed. Find the tension in the threads now.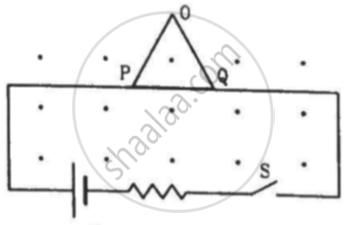
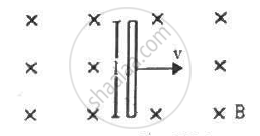
A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, moves with a velocity v,as shown in the figure. (a) Find the average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire. (b) Due to this magnetic force, electrons concentrate at one end, resulting in an electric field inside the wire. The redistribution stops when the electric force on the free electrons balances the magnetic force. Find the electric field developed inside the wire when the redistribution stops. (c) What potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire?
A cyclotron's oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? If the radius of its 'dees' is 60 cm, calculate the kinetic energy (in MeV) of the proton beam produced by the accelerator.
Cyclotron is used to ______.
Cyclotron frequency of a charged particle having charge q and mass m in a cyclotron producing magnetic field B is ______.
A charged particle is moving in a cyclotron, what effect on the radius of path of this charged particle will occur when the frequency of the ratio frequency field is doubled?
The cyclotron was designed by ______
A cyclotron can accelerate ______.
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
