Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
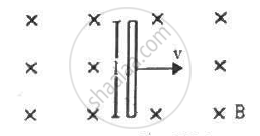
A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, moves with a velocity v,as shown in the figure. (a) Find the average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire. (b) Due to this magnetic force, electrons concentrate at one end, resulting in an electric field inside the wire. The redistribution stops when the electric force on the free electrons balances the magnetic force. Find the electric field developed inside the wire when the redistribution stops. (c) What potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire?
उत्तर
Given:-
Length of the conducting wire = l
Inward magnetic field = B
Velocity of the conducting wire = v
As the wire is moving with velocity v, we can consider this as the net motion of electrons inside the wire with velocity v.
(a) The average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire
= e(v × B) = evB, where e is the charge of an electron.
(b) The redistribution stops when the electric force is just balanced by the magnetic force.
Electric force, F = eE and also magnetic force, F = evB
On equatinging the two forces, we get:-
eE = evB
⇒ E = vB
(c) The potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire:-
V = lE = lvB, where V is the potential difference across the ends of the wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Electrons
(B) Protons
(C) Deuterons
(D) α- particles
State the principle of a cyclotron.
Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Write briefly how this machine is used to accelerate charged particles to high energies
A deuteron and a proton are accelerated by the cyclotron. Can both be accelerated with the same oscillator frequency? Give reason to justify your answer.
A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency?
Consider a 10-cm long portion of a straight wire carrying a current of 10 A placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T making an angle of 53° with the wire. What magnetic force does the wire experience?
Figure shows a rod PQ of length 20.0 cm and mass 200 g suspended through a fixed point O by two threads of lengths 20.0 cm each. A magnetic field of strength 0.500 T exists in the vicinity of the wire PQ, as shown in the figure. The wires connecting PQ with the battery are loose and exert no force on PQ. (a) Find the tension in the threads when the switch S is open. (b) A current of 2.0 A is established when the switch S is closed. Find the tension in the threads now.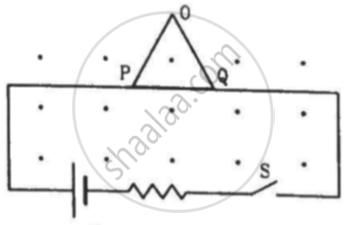
(a) An electron moves along a circle of radius 1 m in a perpendicular magnetic field of strength 0.50 T. What would be its speed? Is it reasonable? (b) If a proton moves along a circle of the same radius in the same magnetic field, what would be its speed?
A cyclotron's oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? If the radius of its 'dees' is 60 cm, calculate the kinetic energy (in MeV) of the proton beam produced by the accelerator.
Cyclotron is used to ______.
Which of the following is not correct about cyclotron?
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Its centripetal acceleration is ______.
A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that, its centripetal acceleration ac is varying with time t as ac = k2rt2, where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particle by the forces acting on it is ______.
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
