Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, moves with a velocity v,as shown in the figure. (a) Find the average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire. (b) Due to this magnetic force, electrons concentrate at one end, resulting in an electric field inside the wire. The redistribution stops when the electric force on the free electrons balances the magnetic force. Find the electric field developed inside the wire when the redistribution stops. (c) What potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire?
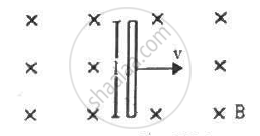
उत्तर
Given:-
Length of the conducting wire = l
Inward magnetic field = B
Velocity of the conducting wire = v
As the wire is moving with velocity v, we can consider this as the net motion of electrons inside the wire with velocity v.
(a) The average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire
= e(v × B) = evB, where e is the charge of an electron.
(b) The redistribution stops when the electric force is just balanced by the magnetic force.
Electric force, F = eE and also magnetic force, F = evB
On equatinging the two forces, we get:-
eE = evB
⇒ E = vB
(c) The potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire:-
V = lE = lvB, where V is the potential difference across the ends of the wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Electrons
(B) Protons
(C) Deuterons
(D) α- particles
State the principle of a cyclotron.
Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
Draw a schematic sketch of a cyclotron. Explain clearly the role of crossed electric and magnetic field in accelerating the charge. Hence derive the expression for the kinetic energy acquired by the particles.
Explain the principle and working of a cyclotron with the help of a schematic diagram. Write the expression for cyclotron frequency.
Verify that the units weber and volt second are the same.
Which of the following particles will describe the smallest circle when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
If a charged particle kept at rest experiences an electromagnetic force,
(a) there must be an electric field
(b) there must be a magnetic field
(c) both fields cannot be zero
(d) both fields can be non-zero
An electron is projected horizontally with a kinetic energy of 10 keV. A magnetic field of strength 1.0 × 10−7 T exists in the vertically upward direction.
(a) Will the electron deflect towards the right or left of its motion?
(b) Calculate the sideways deflection of the electron while travelling through 1 m. Make appropriate approximations.
\[\ce{Fe+}\] ions are accelerated through a potential difference of 500 V and are injected normally into a homogeneous magnetic field B of strength 20.0 mT. Find the radius of the circular paths followed by the isotopes with mass numbers 57 and 58. Take the mass of an ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.
Cyclotron is used to ______.
Cyclotron frequency of a charged particle having charge q and mass m in a cyclotron producing magnetic field B is ______.
A charged particle is moving in a cyclotron, what effect on the radius of path of this charged particle will occur when the frequency of the ratio frequency field is doubled?
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Its centripetal acceleration is ______.
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
