Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
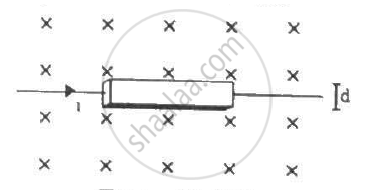
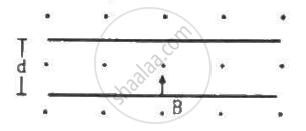
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
उत्तर
Given:-
Width of the silver strip = d
Area of cross-section = A
Electric current flowing through the strip = i
The number of free electrons per unit volume = n
(a) The relation between the drift velocity and current through any wire,
i = vnAe, where e = charge of an electron and v is the drift velocity.
`v = i/(nAe)`
(b)The magnetic field existing in the region is B.
The average magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor,
F = ilB
So, the force on a free electron `= (ilb)/(nAl) = (iB)/(nA)`upwards (Using Fleming's left-hand rule)
(c) Let us take the electric field as E.
So, further accumulation of electrons will stop when the electric force is just balanced by the magnetic force.
`eF= F =(iB)/(An)`
`⇒ E =(iB)/(eAn)`
(d) The potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation will be
V = Er
`⇒ E × d = (iBd)/(eAn)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
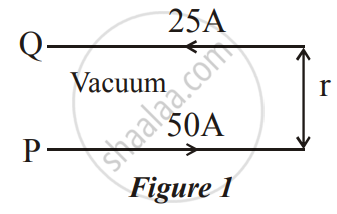
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
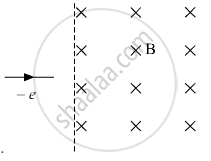
field.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Write the expression for Lorentz magnetic force on a particle of charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field`vecB`. Show that no work is done by this force on the charged particle.
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x−y plane along the curve y = A sin `((2x)/lamda x)`. magnetic field B exists in the z direction. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the portion of the wire between x = 0 and x = λ.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

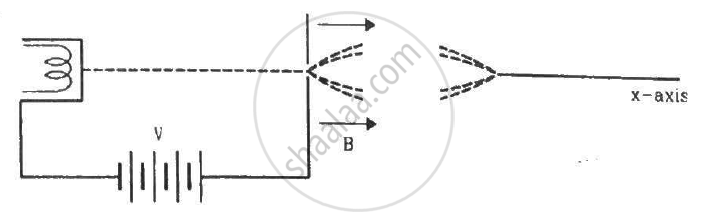
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
A particle with a charge of 5.0 µC and a mass of 5.0 × 10−12 kg is projected with a speed of 1.0 km s−1 in a magnetic field of magnitude 5.0 mT. The angle between the magnetic field and the velocity is sin−1 (0.90). Show that the path of the particle will be a helix. Find the diameter of the helix and its pitch.
A particle of mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a region in which the electric field and magnetic field are given by
`vecB = -B_0 vecj and vecE = E_0 vecK `
Find the speed of the particle as a function of its z-coordinate.
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
