Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
उत्तर
Magnetic field strength, B = 1.5 T
Radius of the cylindrical region, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Current in the wire passing through the cylindrical region, I = 7 A
(a) If the wire intersects the axis, then the length of the wire is the diameter of the cylindrical region.
Thus, l = 2r = 0.2 m
Angle between magnetic field and current, θ = 90°
Magnetic force acting on the wire is given by the relation,
F = BIl sin θ
= 1.5 × 7 × 0.2 × sin 90°
= 2.1 N
Hence, a force of 2.1 N acts on the wire in a vertically downward direction.
(b) New length of the wire after turning it to the Northeast-Northwest direction can be given as:
I1 = `"l"/sin θ`
Angle between magnetic field and current, θ = 45°
Force on the wire,
F = BIl1 sin θ
= BIl
= 1.5 × 7 × 0.2
= 2.1 N
Hence, a force of 2.1 N acts vertically downward on the wire. This is independent of angleθbecause l sinθ is fixed.
(c) The wire is lowered from the axis by distance, d = 6.0 cm
Suppose wire is passing perpendicularly to the axis of cylindrical magnetic field then lowering 6 cm means displacing the wire 6 cm from its initial position towards to end of the cross-sectional area.
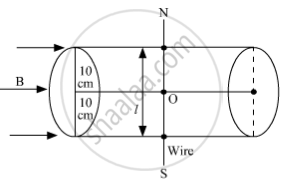
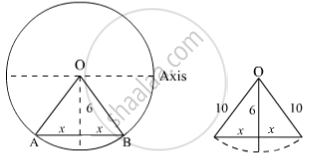
x = `sqrt(10^2 - 6^2)`
= 8 cm
Thus the length of wire in a magnetic field will be 16 cm as AB = L = 2x = 16 cm
Now the force,
F = iLB sin 90° as the wire will be perpendicular to the magnetic field.
F = 7 × 0.16 × 1.5 = 1.68 N
The direction will be given by the right-hand curl rule or screw rule i.e. vertically downwards.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
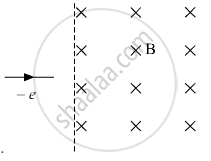
field.
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
A beam consisting of protons and electrons moving at the same speed goes through a thin region in which there is a magnetic field perpendicular to the beam. The protons and the electrons
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
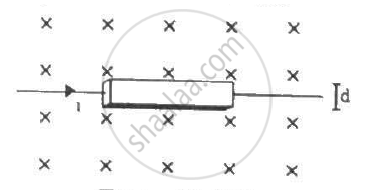
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists in space from east to west. With what speed should a particle of mass 0.010 g and with charge 1.0 × 10−5 C be projected from south to north so that it moves with uniform velocity?
