Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
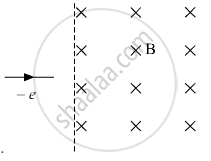
field.
उत्तर
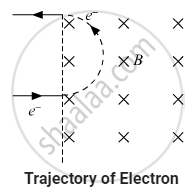
Let the time taken by the electron to come out of the region of magnetic field be t.
Velocity of the electron, v = 4 × 104 m/s
Magnetic field, B = 10−5 T
Mass of the electron, m = 9 × 10−31 kg
We know
\[t = \frac{\pi r}{v}\]
\[\text { where r } = \frac{mv}{Bq}\]
\[\text { Now,} \]
\[t = \frac{\pi m}{Bq} = \frac{3 . 14 \times 9 \times {10}^{- 31}}{{10}^{- 5} \times 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = 17 . 66 \times {10}^{- 7} s = 1 . 76 \mu s\]
Thus, the time taken by the electron to come out of the region of magnetic field is 1.76 μs.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force `vecF` acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving with velocity `vecV` in a magnetic field `vecB` , Under what conditions will it move in (i) a circular path and (ii) a helical path?
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
Using the formula \[\vec{F} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \text{ and } B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\]show that the SI units of the magnetic field B and the permeability constant µ0 may be written as N mA−1 and NA−2 respectively.
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
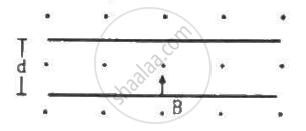
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
