Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force `vecF` acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving with velocity `vecV` in a magnetic field `vecB` , Under what conditions will it move in (i) a circular path and (ii) a helical path?
उत्तर
When a charged particle having charge q moves inside a magnetic field `vecB` with velocity `vecV`, it experiences a force
`vecF =q(vecV ×vecB )`
When `vecV` is perpendicular to `vecB`
The force `vecF` on the charged particle acts as the centripetal force and makes it move along a circular path.
The point charge travels in the plane perpendicular to both `vecV` and `vecB`.
When the component of velocity of the charge particle is parallel to the direction of the force of the electric field, then the force experienced due to that component will be zero, because
F=qvBsin0°=0, and particle will move in a straight line. Also, the force experienced by the component perpendicular to `vecB` moves the particle in a circular path. The combined effect of both the components will move the particle in a helical path.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
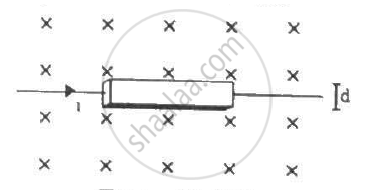
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A particle of charge 2.0 × 10−8 C and mass 2.0 × 10−10 g is projected with a speed of 2.0 × 103 m s−1 in a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T. The velocity is perpendicular to the field. Find the radius of the circle formed by the particle and also the time period.
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.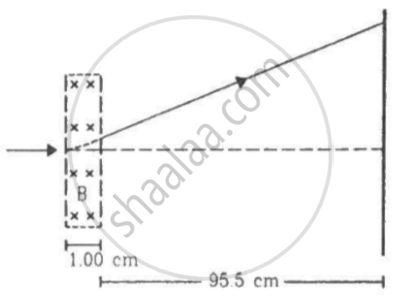
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
