Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
उत्तर
The Lorentz magnetic force is given by the following relation:
`vecF=q(vecVxxvecB)`
Here, q is the magnitude of the moving charge.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane containing the velocity vector `(vecV)`and the magnetic field vector `(vecB)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
An electric current i enters and leaves a uniform circular wire of radius a through diametrically opposite points. A charged particle q, moving along the axis of the circular wire, passes through its centre at speed v. The magnetic force acting on the particle, when it passes through the centre, has a magnitude equal to
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
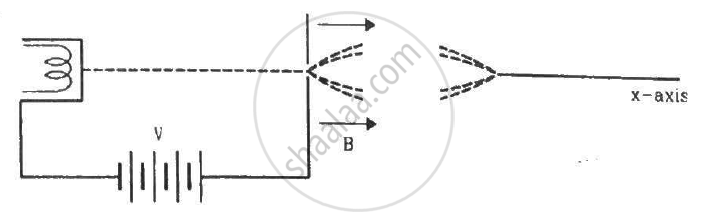
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`